File Locking
File locking ensures consistency and data integrity during concurrent operations, regardless of the access method used (web interface, WebDAV, synchronization, collaborative editors, or API).
Two types of locks are used depending on the nature of the operations: exclusive and shared.
Even when a document is locked by an external source, it remains visible in the web interface and may, in some cases, be subject to specific management actions.

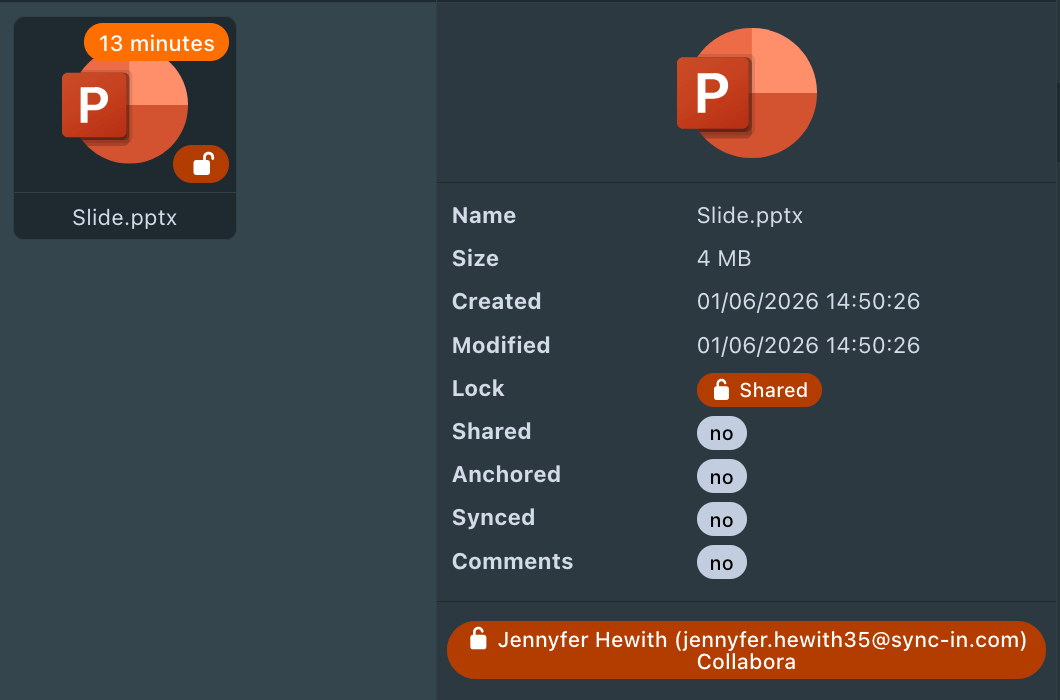
Exclusive Lock
An exclusive lock prevents any concurrent write operation on a file while the lock is active, while allowing read access.
It is used to ensure that a modification cannot be interrupted or conflict with another write operation.
Exclusive lock contexts:
- Creating or updating files (upload via WebDAV or browser)
- File synchronization
- Simple text editing (non-collaborative editor)
An exclusive lock cannot be applied if a lock is already present on the file, regardless of its nature.
Shared Lock
A shared lock allows multiple users to access a file simultaneously in a controlled context. It enables reading and concurrent content modification when the tool supports it.
Shared lock context:
- Collaborative editing via OnlyOffice or Collabora Online.
Shared locks are application-specific to the one that creates them. If a document is locked via OnlyOffice, it cannot be opened for editing via Collabora Online, and vice versa.
Lock Actions

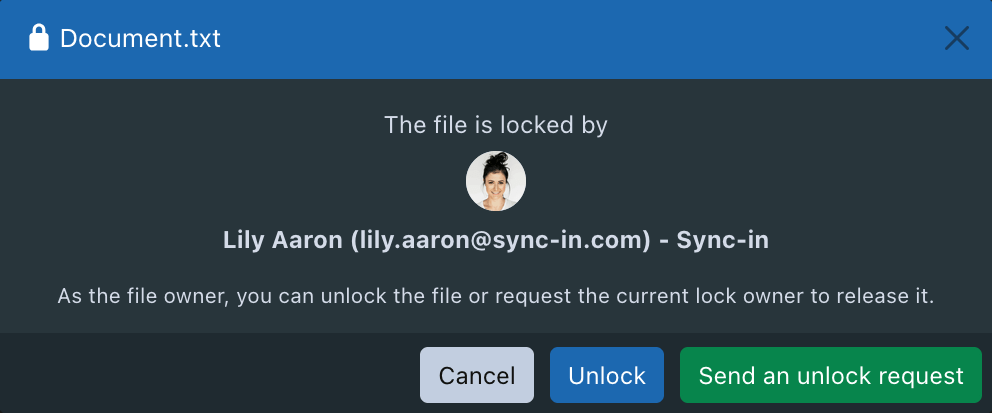
Depending on your role and the lock status, different actions are possible:
- If you are not the lock owner, you can submit an unlock request, which will be sent via notification to the user currently holding the lock.
- If you are the lock owner and the lock is expired or stuck (stale lock), you can force unlock the file, provided that no modification is in progress.